Tuesday, December 18, 2018
Friday, October 5, 2018
A compound produced by bacteria in papayas shows promise as a powerful antibacterial agent
(Natural News) One of the commonly used bacterial species for industrial purposes is Bacillus licheniformis. A specific strain of this species, which was identified and isolated from papayas in Thailand, was shown to produce antimicrobial compounds. For this study, which was published in CyTA – Journal of Food, the antimicrobial compounds produced by the BFP011 strain of B. licheniformis were further characterized and evaluated for antimicrobial activity.
Bacillus sp. serve as sources for naturally-derived antimicrobial compounds, which can come in the form of either peptides or polyketides. Between these two, peptides, such as surfactins and fengycins, are more abundant than polyketides. These antimicrobial compounds are important for their role in the treatment of infections, as well as in food preservation.
In this study, crude extracts were acquired from BFP011 and subjected to further purification to determine the individual compounds present. This was done using thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC). The purified fractions revealed the presence of macrolactins and amicoumacins, which are both non-peptides.
Antimicrobial activity of the crude extracts and the purified fractions were determined against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria that are involved in human pathogenesis or food spoilage. Results showed that the compounds were effective against a variety of bacterial species. However, Gram-negative bacteria were observed to be less susceptible to the extracts than Gram-positive bacteria. This difference in sensitivity can be attributed to lower peptidoglycan content in Gram-negative bacteria, since most antimicrobial compounds work by inhibiting peptidoglycan synthesi.
The mechanisms of action of the purified fractions against Salmonella typhi ATCC 5784 were also determined based on changes in bacterial morphology when viewed under a scanning electron microscope. S. typhi was selected for this part of the study because of its ability to cause human disease and survive in low temperature, which could lead to food contamination. Exposure of S. typhi to the purified fractions led to an inhibition of its growth, showing that macrolactins and amicoumacins are sufficient for antimicrobial activity against S. typhi. It was also observed that cells treated with the purified fractions caused deformation of the cell membrane or formation of protrusions on the surface.
Based on these results, the researchers were able to determine that B. licheniformisBFP011 produces non-peptidic antimicrobial compounds, namely macrolactins and amicoumacins. They were also able to observe that these compounds work against various bacterial species and that their mechanism of action involves the destruction of the cell membrane in a time-dependent manner.
“Notably, the scope of potential applications would not be limited to suppressing the bacterial growth in food products, but also include novel antimicrobial therapeutics, which could help to promote human health by lowering the risks associated to infection with multiresistant bacteria,” the researchers concluded.
Friday, August 31, 2018
Flu-pocalypse: The shocking failure of the flu vaccine exposed
(Natural News) Back-to-school season is here. Alongside sales, shopping and students, you may have noticed that something else is back: The flu shot. The push to get vaccinated is in full swing, whether you’re at the grocery store or simply watching the evening news. “It’s never too early to get the flu shot,” vaccine pushers are saying. And after the massive failure of the 2017 flu shot, it’s no surprise that pro-vaccine propaganda is already everywhere.
As the masses become more aware of the fraud behind the flu vaccine, Big Pharma and their puppets are going to be working overtime to sell their disinformation. In 2017, the flu vaccine was so ineffective that experts warned there would be a “Flu-pocalypse.” As a news video by The Highwire with Del Bigtree shows, media pundits around the world declared that the 2017 flu shot was only about 10 percent “effective,” yet companies and hospitals around the U.S. are forcing employees to get vaccinated.
“It’s a terrible vaccine,” Bigtree states. “But what’s outrageous is how much fear they’re creating around the idea that they may not have a vaccine,” he contends. Indeed, the fear here is actually being used to serve the vaccine industry. It’s as if these people believe the human immune system simply can’t function without a shot.
After years of toxic inoculations, that may not be so far-fetched (unfortunately).
As Bigtree contends, the media seems to use fear-mongering to push people towards vaccination, even when the vaccine clearly doesn’t work. Last year’s vaccine was a total sham — and this year’s inoculation will be no different. But everywhere you look, there’s an advertisement for the shot. Some places are even doling out flu shots for free, but it seems Big Pharma can’t even give these things away anymore.
The flu shot charade
While the mainstream media likes to claim that any increase in the case of flu is a result of people not getting vaccinated, data from the CDC shows that by the end of the flu season, approximately the same number of people were vaccinated in 2017 as years past. While the CDC writes that early season vaccination was lower, the data presented in their charts clearly shows that by the end of flu season, the numbers of vaccinated people are consistently about the same every year:
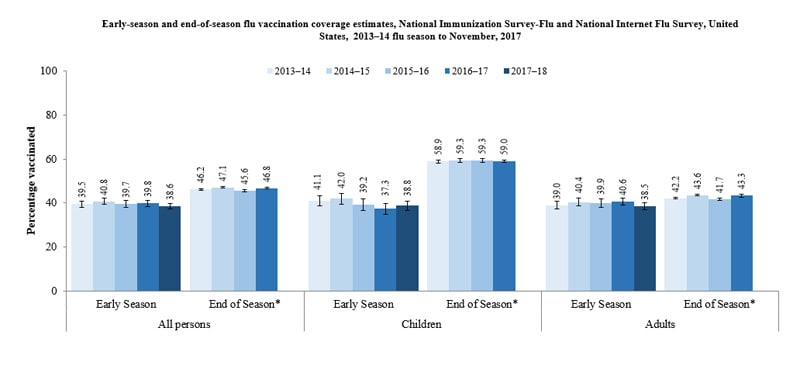
Indeed, the failure of the flu vaccine is not due to a dramatic decrease in the number of people being vaccinated, though that is what the vaccine propagandists would like for you to believe. But as Mike Adams, founder of Natural News and the pro-freedom video-sharing platform REAl.video, reports, the real science on vaccines lies in stark opposition to the pro-vaccine narrative.
Indeed, the failure of the flu vaccine is not due to a dramatic decrease in the number of people being vaccinated, though that is what the vaccine propagandists would like for you to believe. But as Mike Adams, founder of Natural News and the pro-freedom video-sharing platform REAl.video, reports, the real science on vaccines lies in stark opposition to the pro-vaccine narrative.
The Health Ranger writes:
Now a new study conducted by the Scripps Research Institute and published in the science journal PLoS blows the lid on exactly why flu shots are the greatest medical hoax in the history of science and medicine. Titled, “A structural explanation for the low effectiveness of the seasonal influenza H3N2 vaccine,” the research paper concludes that the very method of modern flu vaccine production causes viral strains to mutate to non-effective structures that do not confer the immunity being routinely claimed for flu vaccines.
Essentially, the way flu shots are made renders the flu strains useless for promoting immunity — which is why so many people still get the flu, even after vaccination. This failure rate is then used as propaganda to promote more vaccination.
But as Adams reported earlier this year, studies have now also shown that the flu vaccine doesn’t just fail — it can also cause disease to spread. Once again, mainstream media and conventional medicine have dropped the ball.
Tuesday, June 19, 2018
Mediterranean-style diet found to improve quality of life for people who are depressed
(Natural News) The Mediterranean diet is known to be among the healthiest of diets with a lower incidence of chronic disease and greater longevity. It is considered a “gold standard” in healthy eating.
Traditional Mediterranean diets (MedDiet) are associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, a condition that overlaps with depression. The following study, which was published in the Journal of Nutrition & Intermediary Metabolism, aimed to investigate the effects of the MedDiet on mental health and quality of life in people with depression.
A total of 163 adults aged 18-65 with self-reported depression participated in a randomized controlled trial. The trial provided nutrition education and food hampers and cooking workshops every two weeks for three months, with six months follow-up.
The control group attended social groups every two weeks. During this period, the participants completed mental health, quality of life and dietary questionnaires. Data were analyzed using linear mixed modeling and Pearson correlations.
The treatment group was found to have a higher MedDiet score; consumed more vegetables, fruits, nuts, whole grains, and legumes; consumed a greater diversity of vegetables and fruit; and had less unhealthy snacks and red meat/chicken, in comparison to the control group at three months.
Moreover, the treatment group had reduced depression scores and higher mental health and quality of life scores.
The findings indicated that reduced depression scores correlated with increased MedDiet, consumption of nuts, legumes, and a greater diversity of fruits and vegetables.
More on the Mediterranean Diet
MedDiet is primarily plant-based, with emphasis on fresh vegetables and fruits, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes (beans and lentils). However, meat is not entirely taken out of the picture with this diet.
Fish and seafood are the primary sources of animal proteins and are recommended for consumption several times per week. Chicken is also included in this diet, eaten about once or twice per week, as well as eggs, eaten in moderate amounts (generally about seven eggs per week, including those used in baking). Meanwhile, red meat and sweet desserts are consumed in small amounts, only a few times per month. Desserts generally consist of fresh seasonal fruits.
Cheese and yogurt are great sources of probiotics and are eaten in small to moderate amounts anywhere from daily to weekly. Olive oil is the main source of fat and is used in cooking and on salads, while honey is the primary sweetener (but is used sparingly). Wine is consumed in moderation – one to two glasses per day for men and one glass for women – and usually with meals.
Among the many health benefits of MedDiet, it has also been shown to help decrease the risk of anxiety and depression. This type of diet is rich in the nutrients that are critical for the regulation of mood by providing the necessary fiber and probiotics involved in proper digestion, which in turn help reduce stress and enhance mood.
Reap the benefits of MedDiet today by considering to grow your own food, or shopping at your local farmers market to ensure fresh produce. In addition, including more fish and seafood in your daily meals while avoiding processed food is a great first step towards better mental health.
Keep abreast on other healthier food options for the mind at Veggie.news.
Sources include:
Thursday, April 5, 2018
An apple a day really does work: The flavonoid-rich fruit improves cardiovascular health, decreases risk of disease
(Natural News) Apples once again show that they can keep the doctor away. A study has found that the flavonoid-rich fruit enhances cardiovascular health and reduces the risk of disease by improving endothelial function. Just eat it with its skin for more benefits.
Past studies have shown that there is an inverse association between apple consumption and cardiovascular mortality. Endothelial dysfunction is an independent indicator of cardiovascular risk. Therefore, a team of researchers from Australia investigated whether four weeks of constantly consuming apples would enhance endothelial function and blood pressure in individuals with one or more risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
In the randomized, controlled, cross-over trial, 30 individuals with at least one cardiovascular disease risk, such as increased blood pressure, increased blood sugar, increased total cholesterol levels, or central obesity, ate either apples with skin or apple flesh only as a control.
The research team assessed acute and chronic changes in blood pressure, endothelial function, arterial stiffness, and levels of plasma flavonoid metabolites, cholesterol, glucose, nitrate, and nitrite. In addition, they looked at the changes between interventions by mixed models ANOVA with adjustments for baseline.
The findings of the study revealed that endothelial function greatly improved two hours after acute consumption and after chronic consumption of apple with skin in comparison to eating apple without the skin. Yet, there were no significant changes observed in other measurements.
The researchers concluded that their study’s findings support the theory that flavonoid-rich foods prevent cardiovascular disease by enhancing endothelial function, both in the short-term and long-term consumption. (Related: Dietary flavonoids lower heart disease and stroke risk by nearly twenty percent.)
If you want to keep your heart healthy, eat more fruit. A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that eating more fruit may lower your chance of developing major heart disease. Fruit is believed to contain high sugar levels, which is why some people eat it sparingly. However, this study suggested that people should not worry about it.
The study authors from China recruited 512,891 adults aged 30 to 79 years from 10 different localities in China. After a follow-up, 5,173 deaths from cardiovascular disease, 2,551 incident major coronary events, 14,579 ischemic strokes, and 3,523 intracerebral hemorrhages were recorded among the 451,665 participants who did not have a record of cardiovascular disease or antihypertensive treatments at baseline.
Results showed that 18 percent of the participants reported eating fresh fruit daily. Moreover, individuals who regularly ate fresh fruit had lower systolic blood pressure and blood sugar levels as well as a 40 percent lower risk of cardiovascular death in comparison to those who never or rarely at fresh fruit.
The findings of the study are in line with several previous studies that show that increased fruit intake reduces the risk of chronic disease, such as cardiovascular disease, erectile dysfunction, some cancers, and gallbladder problems that require surgery.
“I recommend that people freely consume fresh, whole fruits as snacks—but not fruit juices, smoothies, or other fruit drinks,” said nutrition expert Dr. Thomas Campbell of the University of Rochester Medicine, who was not part of the study.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)




